Example design of a permeability test:
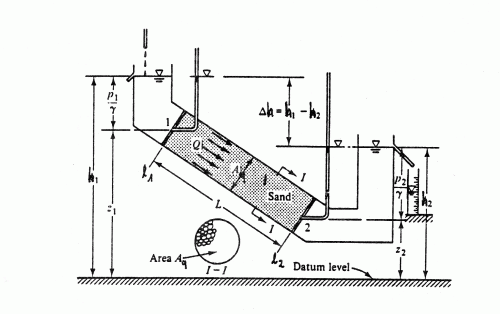
Quantities describing the permeability test (from: Bear, 1979)
The hydraulic conductivity values defined in SPRING via the KWER, KWEV and KFVH attributes are applicable to isotropic flow conditions. This means that irrespective of the flow direction the same flow rate is maintained. Anisotropy can be included for the two-dimensional case by assigning the ZONE and MATE.attributes.
In the vertical direction, the horizontal hydraulic conductivity is used to scale the vertical hydraulic conductivity using the data type KFVH, which provides a ratio between the two hydraulic conductivity values.
For the three-dimensional case, anisotropic flow conditions can be taken into account via the menu item Attributes  Extras
Extras  Anisotropic conductivities. This menu item is activated as soon as the attribute Z-KA is assigned.
Anisotropic conductivities. This menu item is activated as soon as the attribute Z-KA is assigned.
It is also possible to adjust the K-values according to the geological structure of the model layers, and thus the element geometry. If the K-values of ALL layers are to be corrected based on the geometry, this is done by making additional entry at the end of the batch file sitra.bsi
ROTATION KWER
The individual layers can be handled in different ways by using the Z-KA attribute and the menu item Attributes  Extras
Extras  Anisotropic conductivities….
Anisotropic conductivities….
