Attribute:
MATE [-], (element wise) (horizontal or vertical models)
Anisotropy can only be taken into account for the horizontal models using this data type.
K-values and the associated angles/directions are assigned to each zone code (ZONE) for this data type. The material data (MATE) must include the attribute zone codes (ZONE). The unit of the K-values is m/s.
Example:
ZONE identification number
1 7- 11, 15
10 16- 20
10 1- 6, 12- 14
MATErial data
1 0.005 0.005 0.0
10 0.001 0.0009 30.0
In the above example, elements 7 to 11 and 15 have the same K-value of 0.005 m/s in the x- and y-directions without rotation. Elements 1 to 6 and 12 to 14 as well as 16 to 20 are anisotropic.
If only one material is present over the entire model domain then only one entry is required with an associated identification number for this material.
If the angle is not equal to 0, or if the hydraulic conductivity in the x- and y-directions differ, material data will be fixed and will not be iterated during calibration.
!
The following figure illustrates the geometry associated with anisotropy assignment:
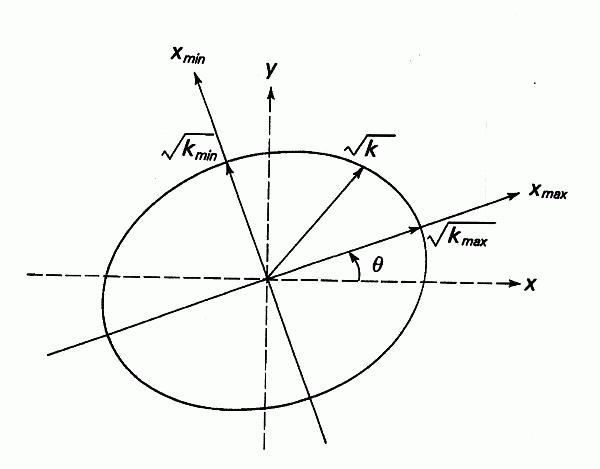
The geometry of anisotropy in two-dimensions
The axes Xmax and Xmin denotes the X- and Y-axes, which are rotated by the angle  .
.
Kmax and Kmin denote the maximum and minimum hydraulic conductivity values in the direction of the respective axes. K is the resulting effective hydraulic conductivity in the direction of flow, which is calculated within the flow calculation.
The anisotropic material values can be entered manually in the *.net file or assigned automatically via the menu item Attributes  Extras
Extras  Anisotropic conductivities....
Anisotropic conductivities....
