In addition to geometric position information, structures also contain values which, together with the structure identifier, enable these values to be assigned to mesh nodes or elements.
Displayed structures can be selected with Pick. Via the menu items List or All... menu items, individual or all structures can be selected for assignment. An input window for defining the assignment parameters then appears:
For point structures:
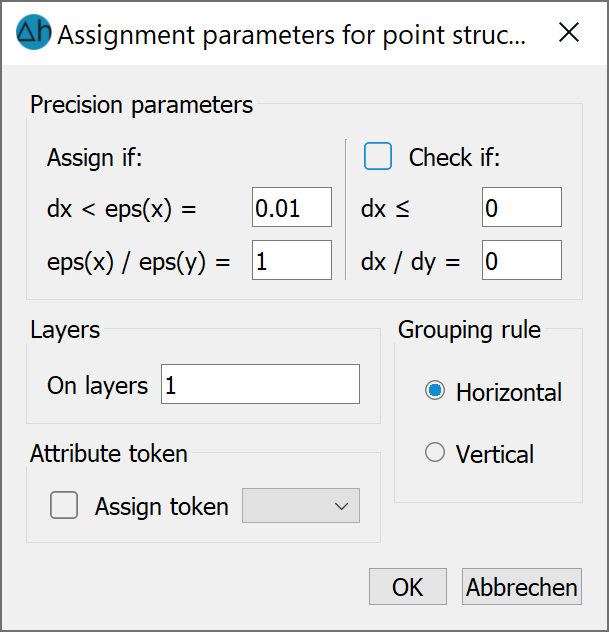
Description of the dialogue inputs using the above example for the assignment of point structures:
Assign point structures:
If the attribute is a node data type, the data identifier is automatically assigned for all nodes with a maximum horizontal distance of dx < eps(x) to a structure point with a defined value.
For element data types, the element centre point must be at a maximum distance dx < eps(x) from the structure point for the purpose of assignment.
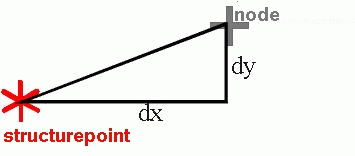
Distance definition for the assignment of structural data
If the ratio eps(x)/eps(y) = 1, then data is assigned to all nodes or element centres within a circle with radius dx around the structure point. However, if the distance dx < eps(x) = 60 m and the ratio eps(x)/eps(y) = 10, then data is assigned to all nodes or element centres within an ellipse with a semi-axis value x = 60 m and y = 6 m around the structure point. If, for example, the distance dx < eps(x) = 60 m and the ratio eps(x)/eps(y) = 0.1 is set, then data is assigned to all nodes or element centres within an ellipse with a semi-axis value x = 60 m and y = 600 m around the structure point.
The assignment control can be used to determine a tolerance limit in which nodes or element centres that have a slightly greater distance than dx to a structure point are still assigned structure data after a query.
For 3D models, the node or element layer must also be specified. It is also possible to specify several layers at once (layer numbers separated by a comma, semicolon, or connected by a hyphen). The data can be grouped horizontally or vertically immediately.
Depending on the data type, the appropriate attribute character can be assigned immediately.
Assign line structures:
The dialogue corresponds to that of the point structure assignment, with the exception of the point-specific properties.
Assigning line structures only makes sense if the line structures have the identifier of a node data type.
To assign a line structure, it must have a defined value for at least one structure point.
All nodes that are close enough to the structure line according to the distance definition above are automatically assigned a value for the corresponding identifier.
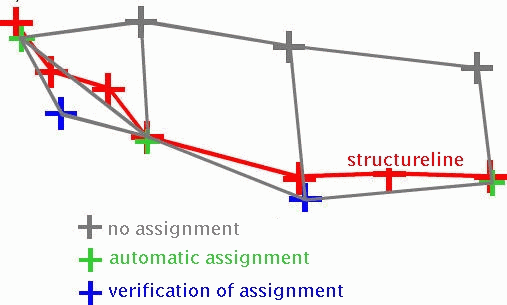
Assignment of structural data for line structures
The data is assigned differently depending on the data type:
In the case of single node data, the value is calculated by linear interpolation or extrapolation of the occupied structure values.
In the case of polygon course data and group data, all nodes that lie within a value range of the structure receive the corresponding value of this value range.
Caution: Structure data for polygon course data or group data identifiers (e.g. LERA, MXKI or BILA) are divided into value ranges during assignment. These ranges extend between two structure points with different entries. Exactly these values are assigned without any interpolation being carried out. The result is structures that have a constant value in some areas. From value range to value range, value jumps occur in the structure points with new values.
Assign area structures:
Assigning area/surface structures is only possible for single data and group data identifiers. Each node that lies within or on the edge of the area structure, or each element whose centre point lies within or on the edge of the area structure, is automatically assigned a value. There is no accuracy query or assignment check for area structures as there is for line or point structures.
The assigned value of the identifier at the corresponding node is calculated as follows:
With group data, all nodes or elements in the area receive the first value defined at a corner point of the area structure.
In the case of single-value data, the first three values at corner nodes of the surface structure are used to define an "inclined plane". The value in the node or element then results from the position of the node or element centre point in this inclined plane. If the surface structure only has a defined value at one corner point or if the first 3 values found are the same, all nodes/elements are assigned a constant value. If more than 3 values are found, these values are not included in the calculation. If only exactly 2 values are found, the second value is not interpreted; only the first value is assigned a constant value.
Attention: Only one value is used when assigning area structures for group data identifiers (e.g. BILA).
Caution: In the case of area structures for single node or element data identifiers, only a maximum of three values are used when assigning. It is therefore possible, but not sensible, to define values at more than three structure corner points.
The correct assignment of polygon course and group data can be checked at Attributes  Extras
Extras  Check group attribute respectively polygon line attribute. If the generated attributes overlap with existing attributes of the same data type, the affected attributes are displayed as green lines and the conflict nodes with green circles.
Check group attribute respectively polygon line attribute. If the generated attributes overlap with existing attributes of the same data type, the affected attributes are displayed as green lines and the conflict nodes with green circles.
