Heat conduction
SPRING-help >> Heat transport >>
The heat flow due to the thermal conductivities of both the fluid jm,w and the matrix jm,s is described by Fourier's law (1822):
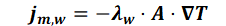
and 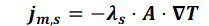
with
jm,w = heat flow in the fluid [W]
jm,s = heat flow in the matrix [W]
λw = thermal conductivity of the fluid [W/(m K)]
λs = thermal conductivity of the matrix [W/(m K)]
A = cross-section of flow [m²]
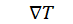 = temperature gradient [K/m]
= temperature gradient [K/m]
This part of the energy flow is independent of the movement of the water. Analogous to Darcy's law, the negative sign results from the fact that the energy flow occurs from high to low temperatures and the temperature gradient is opposite.
 Hydromechanic dispersion
Hydromechanic dispersion