Radioactive or biological decay (half-life calculation)
Radioactive or biological decay (e.g. by bacteria) usually involves an exponential decay rate, which is described by the half-life.
The half-life T1/2 is the time in which a value that decreases exponentially with time has halved.
The half-life calculation is based on an exponential approach function:
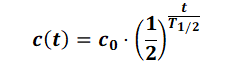
This means:
c(t) = concentration as a function of time [kg/kg]
c0 = initial concentration [kg/kg]
t = time [s]
T1/2 = half-life [s]
In the example, the half-life was set to 5000 seconds:
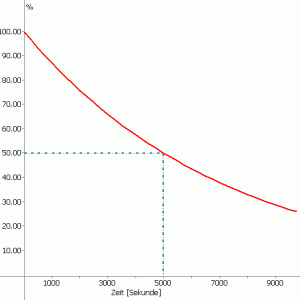
The T1/2 parameter of the function is defined in the Advanced - Half-life (Production/degradation).
 Equation of the mass transport
Equation of the mass transport
