Call via: SPRING  Calculation
Calculation  Mass transport computation
Mass transport computation
The spread of dissolved substances (mass transport) in a porous medium is influenced by the processes of so-called conservative transport processes (advection, diffusion and dispersion) and so-called non-conservative transport processes (adsorption and chemical and biological degradation reactions (production and decomposition).
Substances that are transported and stored exclusively in the pores of the porous medium (only conservative transport processes) are referred to as ideal tracers.
The non-conservative transport processes cause a retention (retardation) or a reduction of the substance content in the groundwater.
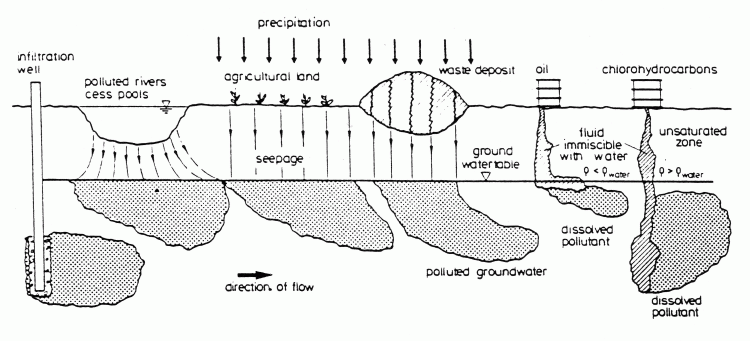
Possible types of substance input into the groundwater
Each transport model is based on a flow model, so that both the parameters for describing the material behaviour in the groundwater are necessary and all the information required for flow modelling must be available.
The substance transport calculation requires the definition of at least one of the attributes KONZ (inflow concentrations) or 1KON (concentration as boundary condition of the first kind.
