When importing structures, you can choose between several data formats:
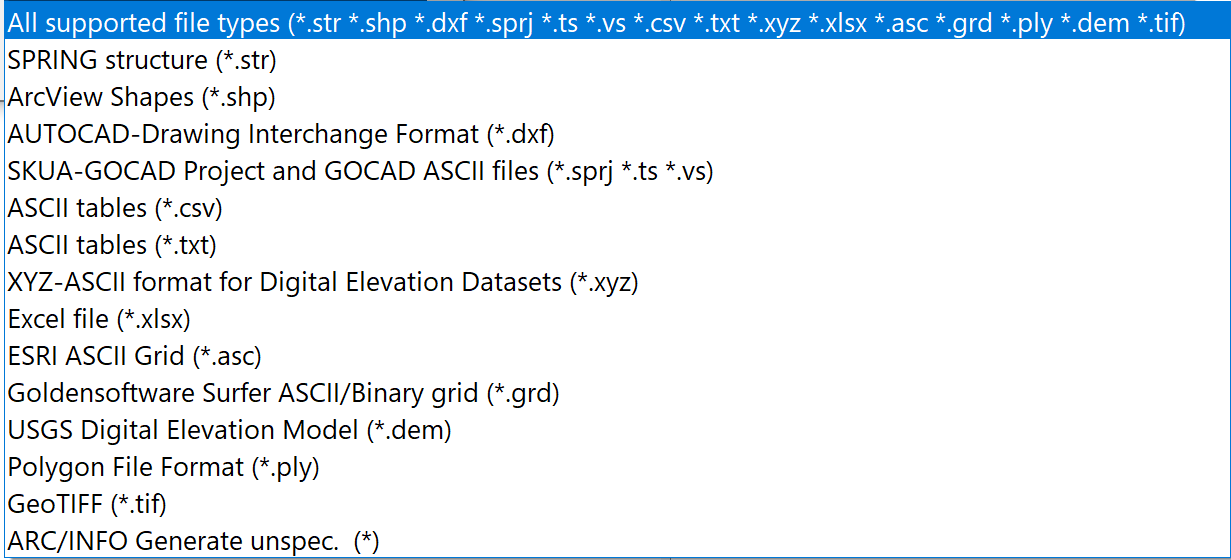
While there are no further queries for the structure data format, further input windows for reading in the files appear for the "SPRING-foreign" formats.
ArcView Shape format (*.shp)
Point, line or area information that is available in ArcView Shape format can be adopted as structures.
After selecting a *.shp file, the following input window appears:
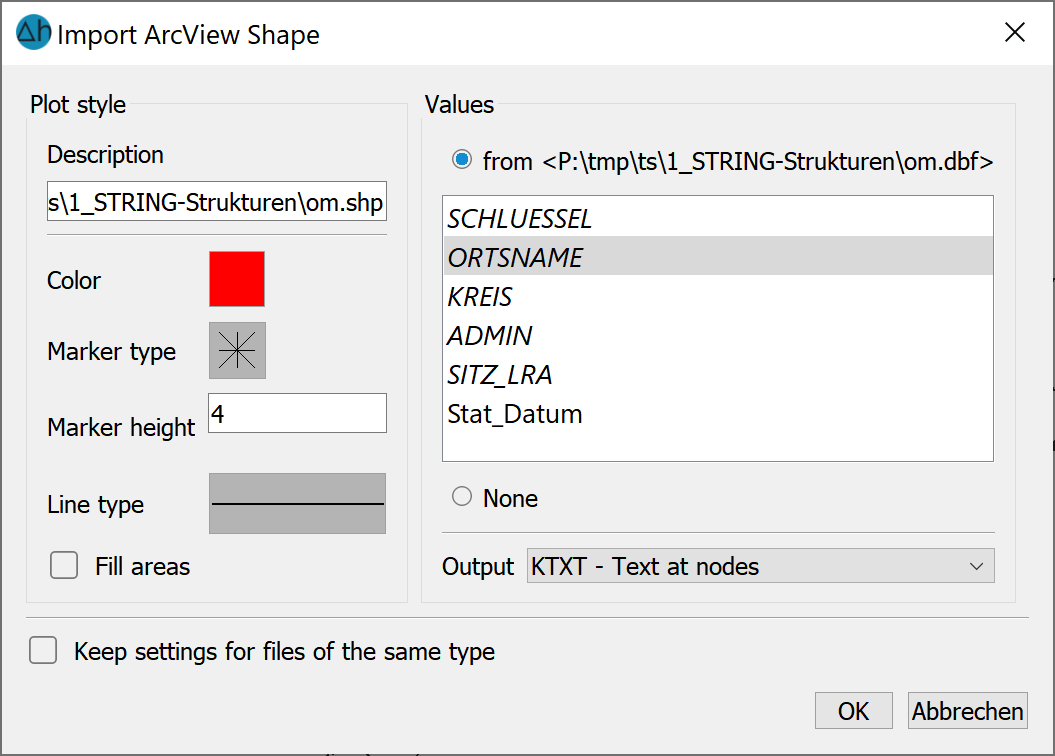
As when editing a structure, the display attributes can be selected here and the value and attribute assignments can be made. Values of the shapefile that are shown in italics are text attributes. These can be adopted as structural values via the data type KTXT or ETXT.
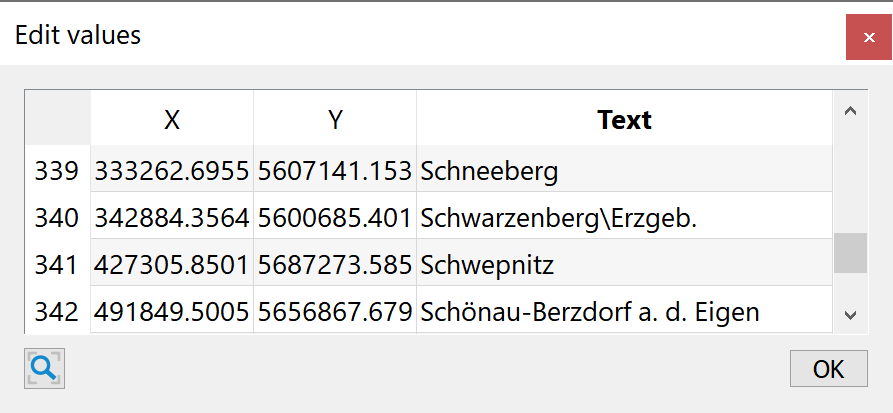
In the illustration, this looks like this, for example:

Angle and color of the structure texts can be edited via View  Attributes...
Attributes...  KTXT/ETXT.
KTXT/ETXT.
Interpolation of texts on a line structure is also possible.
AUTOCAD *.dxf-format
Point, line or surface information that is available in AUTOCAD *.dxf format can be transferred as structures.
After selecting a *.dxf file, the following input window appears:
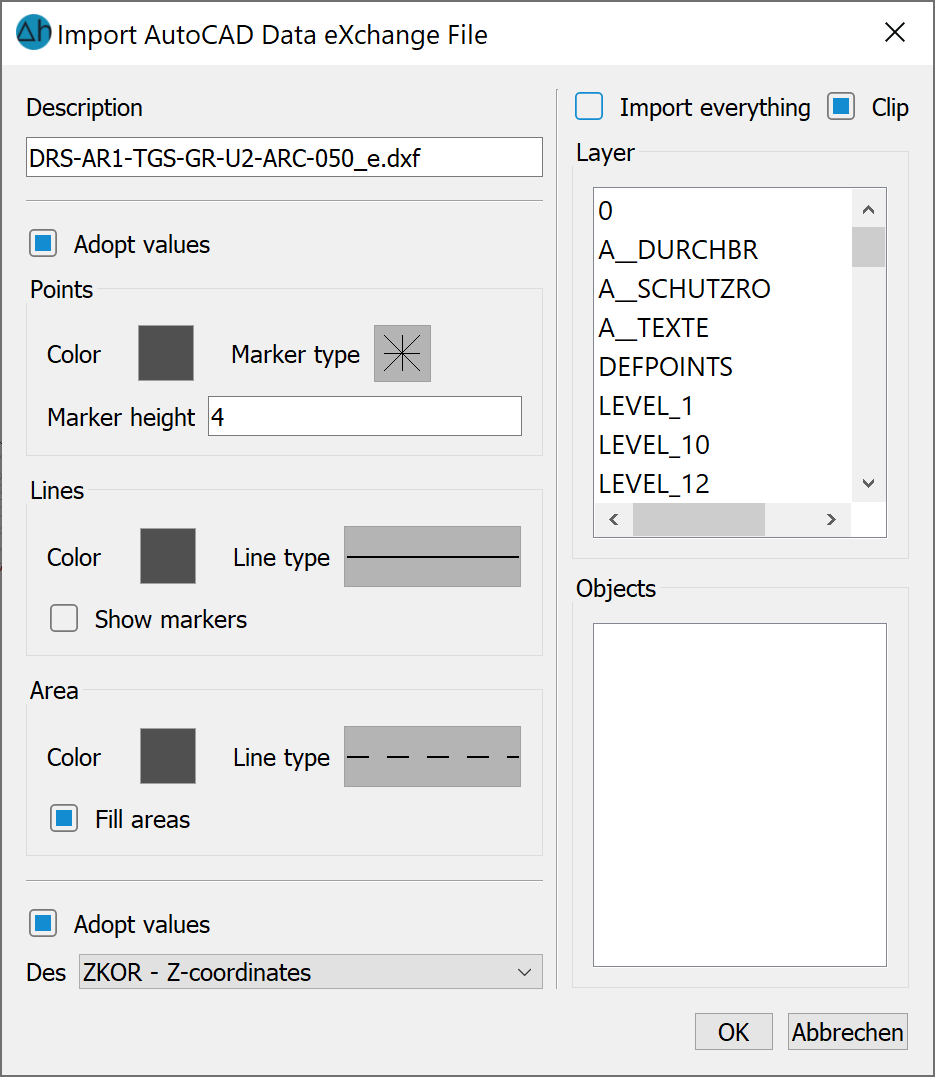
In addition to the display attributes for the different structure types and the attribute assignment, you can select whether all layers of the *.dxf file or only individual ones are imported using a list selection. The values can also be transferred if desired.
SKUA-GOCAD Project and GOCAD ASCII files (*.sprj *.ts *.vs:
Both an entire project (*.sprj) and individual GOCAD files can be imported.
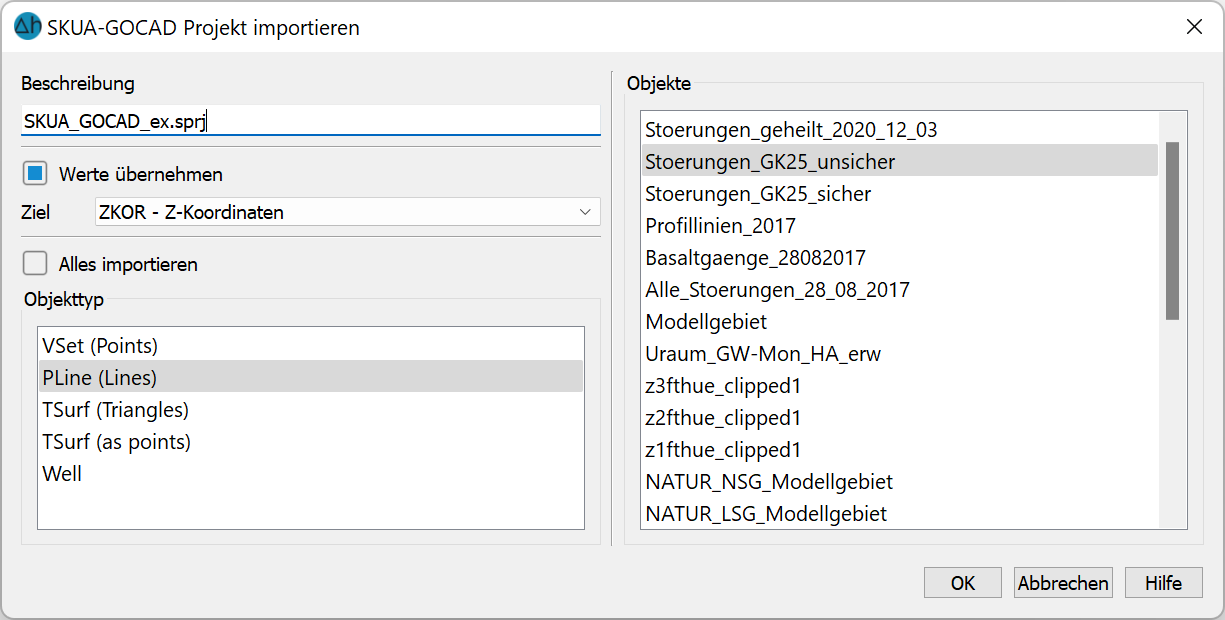
The objects can be imported completely (Import all) or individually.
ASCII-Tables *.csv-format:
Data from database applications is often used as structures for project creation. In this case, it is possible to import the corresponding data (coordinates and any values at the coordinates) in tabular form from an ASCII file.
This can be in the form of comma-separated text (comma separated value: *.csv format). Such data can then be read into SPRING as point structures.
After selecting a *.csv file, the following input window appears:
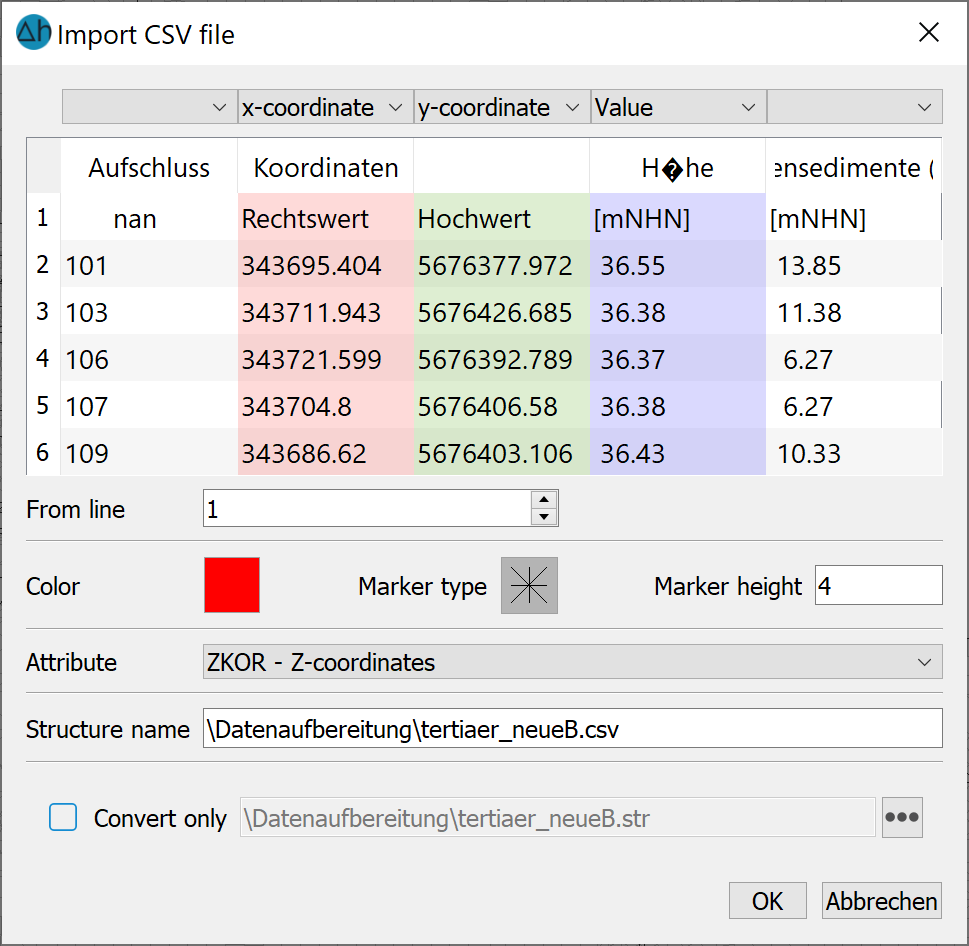 Here the user must enter explicitly to which column the x and y coordinates and z values are assigned. The used decimal and column separator is indicated. A coloured marker is assigned to the data type by which the data points are shown.
Here the user must enter explicitly to which column the x and y coordinates and z values are assigned. The used decimal and column separator is indicated. A coloured marker is assigned to the data type by which the data points are shown.
ASCII-tables *.txt-format:
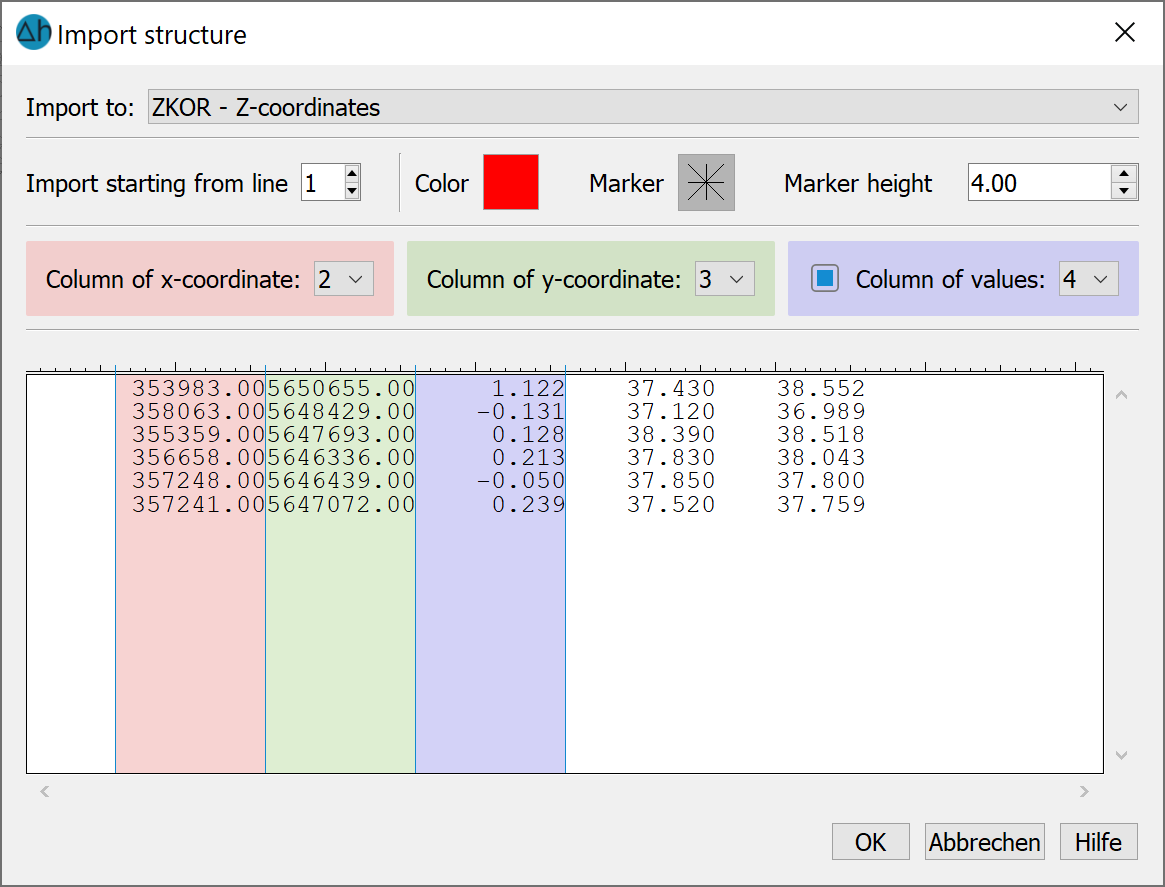
The format of the txt file must contain the values (x, y and, if applicable, z) in blocks of columns. The respective column is manually assigned to the x and y coordinates and the z values. The column width can be changed. The data type can be assigned a coloured marker with which the data points are displayed. The data can be imported starting from a specific line. If there are headers in the file, the import should start from line two.
Finally, the data type to which the z values are to be assigned is selected.
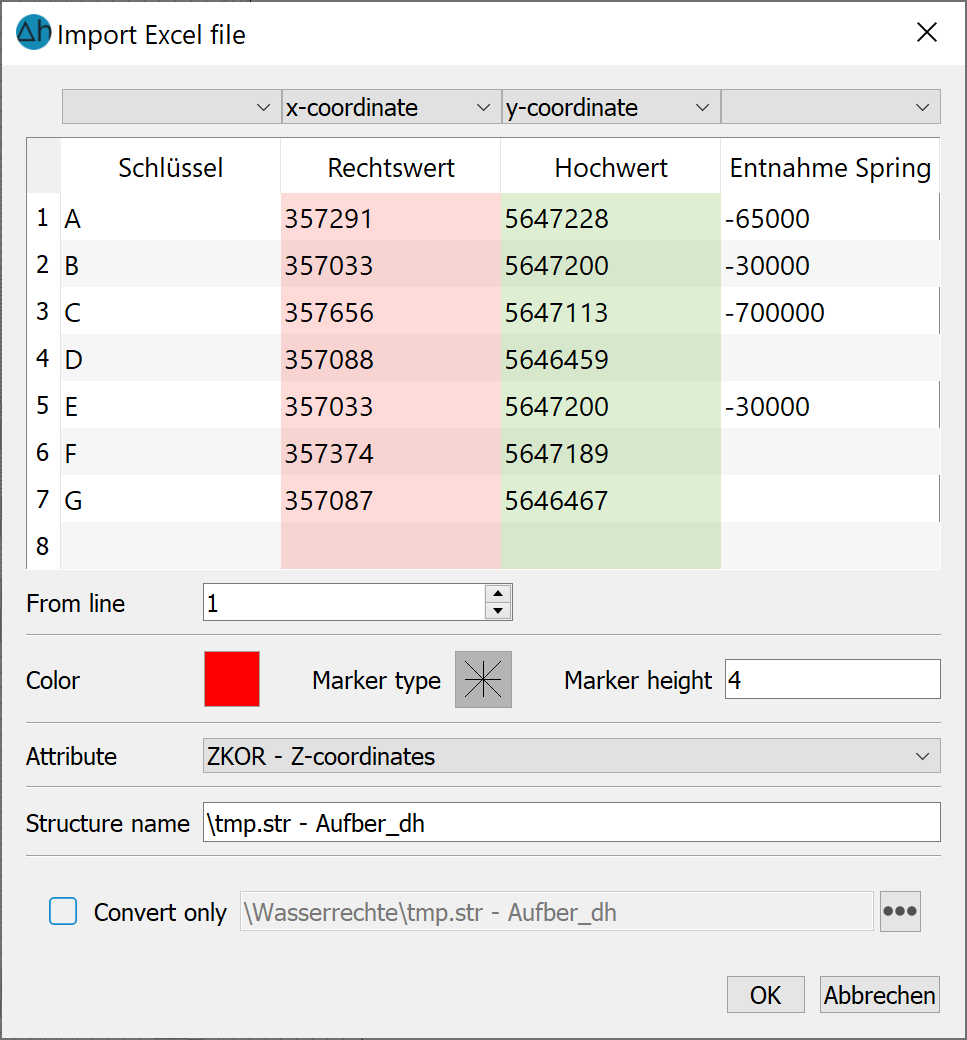
Excel table (*.xlsx)
An Excel table (*.xlsx) can be imported in the same way as a csv file after selecting the appropriate columns.
Please note: The following file formats: ESRI ASCII, Surfer, USGS, GeoTIFF and ARCINFO generate are read in directly without further queries.
