The map menu can only be selected in plot file mode. The following menu items are available:
Arrangement
The following functions are available in the submenu:

If several maps are loaded, the position of the active map can be changed by activating the individual menu items.
The order in which the graphic objects are displayed on the screen and on the output device depends primarily on the order of the objects in the read graphic files. If several maps are read/overlaid one after the other, the maps read last are also displayed last. The display sequence determines which objects can obscure others. This is particularly important for filled areas or lines that overlap exactly.
Edit
The following submenu appears:
Scale…, Scale (with attributes)…
If a map is to be displayed at a different scale, this is possible using the Scale function. If more than one map is available, the map to be scaled must first be identified with the cursor. The desired scale figures are then entered in the input window that appears:
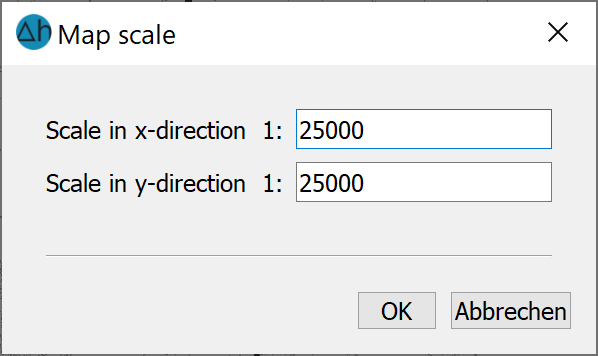
It is possible to scale the two coordinate axes independently of each other.
If the object attributes are also to be scaled when the map is scaled (in particular text heights, marker heights and line widths), Scale (with attributes)… is required.
Scale attributes
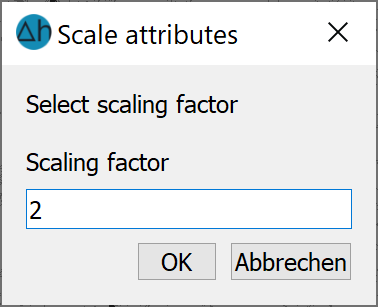
Text heights, marker heights and line thicknesses in a map are often generally too small or too large. Using this menu item, all attributes of a map can be enlarged (scaling factor > 1.0) or reduced (scaling factor <1.0) by entering a scaling factor. The map retains its scale.
If there is more than one map, the map whose attributes are to be scaled must be identified with the cursor. The desired scaling factor for the attributes is then requested with the following input window:
Fit into place
With the Fit into place… menu item, the coordinate system of a map can be fitted over another map, for example, in preparation for overlaying:
The procedure for fitting a map is identical to that of the menu item Bitmap ( Fit into place
Adjust scale
When importing files without scale information (e.g. structure or dxf files), the scale 1:10,000 is always assumed. To avoid errors when calculating distances or areas, for example, the scale can be changed using this function. Once the corresponding map has been identified via an object with the cursor, the scale figures can be corrected in an input window.

Reduce
To single plot layer:
Objects can only be moved in sequence within a layer. However, it is often necessary to move individual objects of a layer in front of objects of another layer. This menu item is helpful for this: If more than one map is loaded, the corresponding map is identified by clicking on the object with the cursor. All layers of this map are then reduced to one layer, i.e. the layer structure of the map is lost.
To a single map:
Several imported maps can be reduced to one map using this menu item. For example, if a logo has been painstakingly positioned as a separate map in the text field of a map by adding it and then scaling and moving it, it is often desirable to save a map frame created in this way for overlaying on other maps or to move it as a unit. The "logo" map should then be integrated into the actual map. To reduce all loaded maps to the coordinate system of a reference map, the reference map whose coordinate system is to be retained is identified by clicking on the object with the cursor. All maps are then reduced to this map, i.e. the coordinate systems of the other maps are lost.
Delete, Move
To delete a map, it is identified using the cursor.
In principle, moving a raster within a map only makes sense if several rasters are already displayed. To identify the raster to be moved, a graphic object belonging to the map in question must be selected. By holding down the mouse button, the bordering rectangle of the card is moved to the new position. Releasing the left mouse button ends the operation and the raster is redisplayed at its selected position.
 Layer
Layer