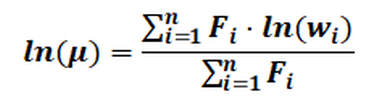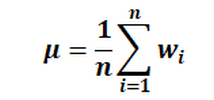The following submenu appears:

Element  node, Node
node, Node  element
element
These menu items can be used to convert element attributes to node attributes or node attributes to element attributes.
The following input windows appear in a 3D model:
|
|
|
|
|
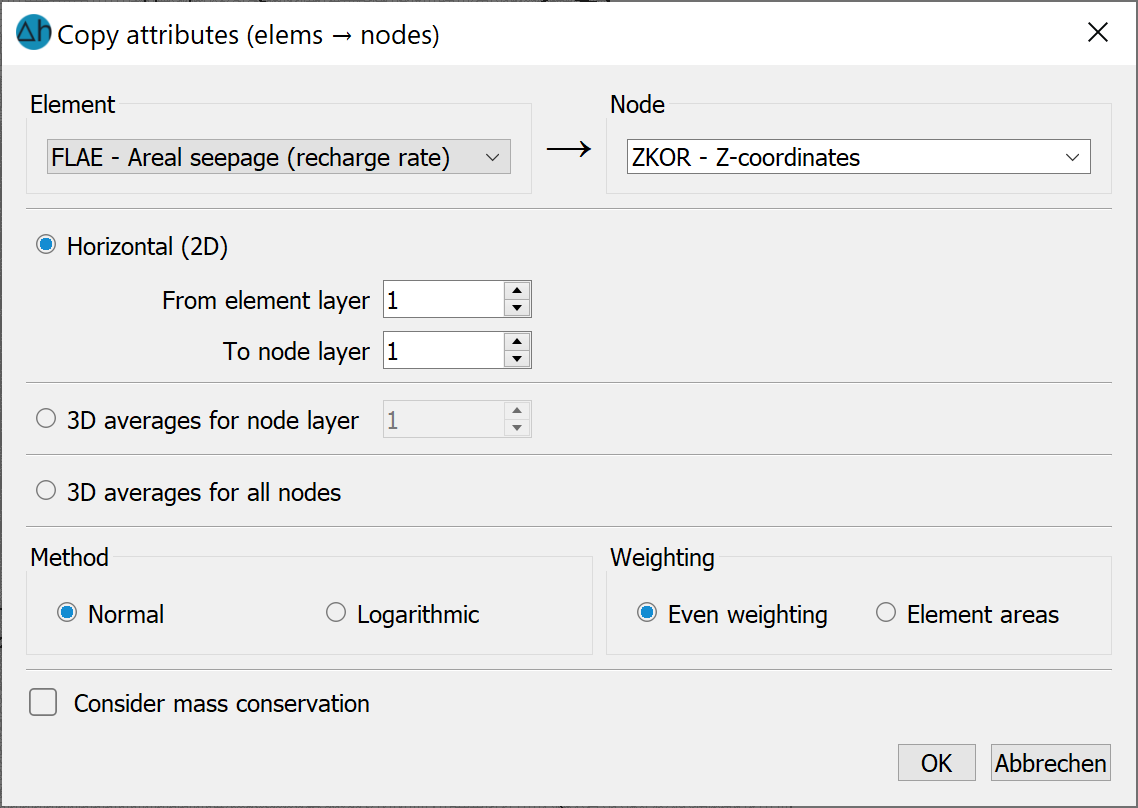
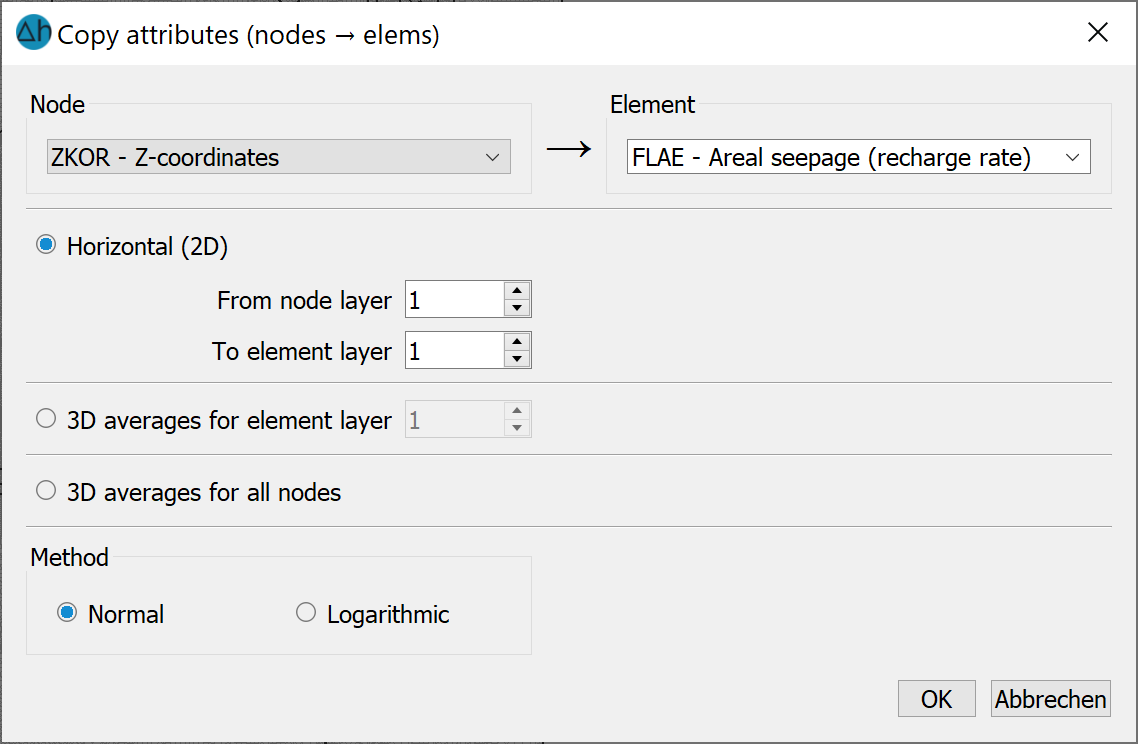
First, the attributes to be copied are defined. |
||
|
For a 3D project, you can choose between 3 mean value calculations: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You can choose between a normal and a logarithmic mean value determination: Normal (arithmetic) mean value μ:
where wi are the neighbouring node or element values that have been converted and n is the number of neighbouring nodes/element values. Logarithmic mean value μ:
where wi are the neighbouring node or element values, to be converted and n is the number of neighbouring nodes/element values. This method is particularly suitable for positive element values with different orders of magnitude, e.g. hydraulic conductivity values. |
||
|
When converting element values to node values, either an equal weighting or a weighting with the element areas Fi can be carried out. With equal weighting, the calculated average value remains unchanged. Weighting using the element area is carried out using the calculation rule: Normal:
Logarithmic:
Where Fi is the area of the neiboughring elements. |
When converting node values to element values, only a normal (even) weighting is possible:
, where wi is the neighbouring node values that are to be converted and n is the number of neighbouring nodes/element values.
|
|
|
Consider mass conservation: If mass conservation is to be taken into account (e.g. when converting from FLAE to KNOT), the element values (e.g. inflow rates) are distributed proportionally to the corner nodes of the element. The area weighting and the choice of averaging (logarithmic/normal) has no significance in this case. A node receives a quarter of the element set from a neighbouring quadrilateral, a third of the element set from a neighbouring triangle and so on |
|
|
Nodes  1D fractures
1D fractures
With these menu item, node data can be copied to 1D fracture attributes..
Node wise or element wise
These menu items can be used to copy one or more attributes of a specific node (base node) or a specific element (base element) to other nodes or elements. This base node / base element is selected by snapping or entering the node / element number.. An input window appears with the existing attributes of the selected node or element:
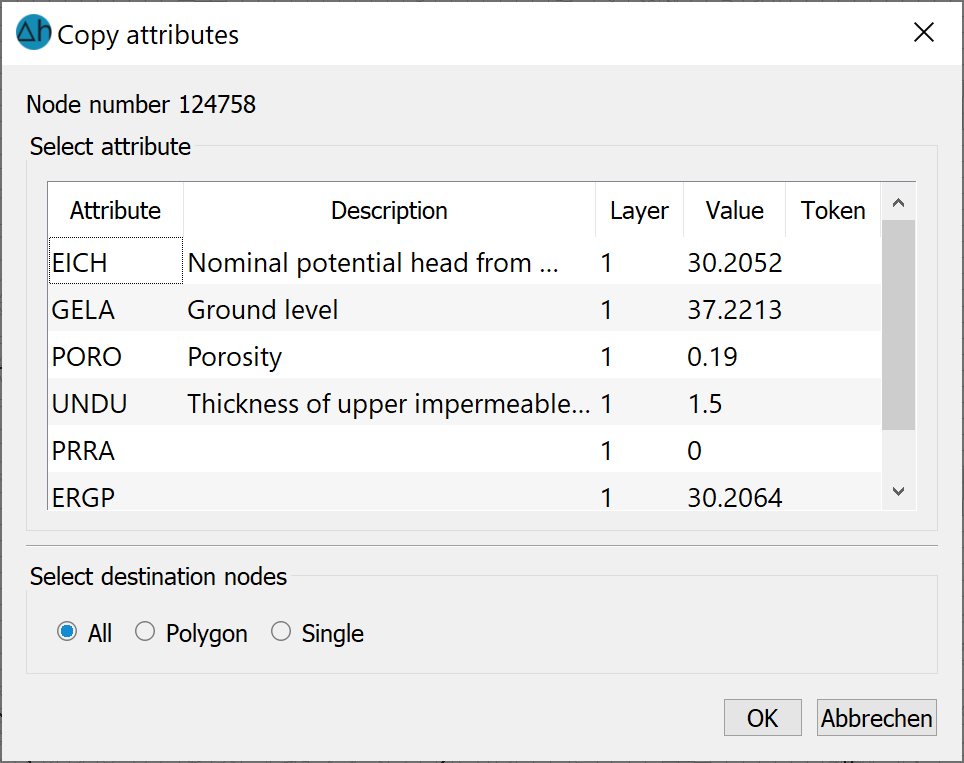
One or more attributes can be selected for copying from this list (use CTRL + SHIFT keys if necessary). The selected attributes can either be assigned to individual nodes/elements or to a range of target nodes/elements. Alternatively, the selected attributes can also be assigned to all nodes/elements.
Attribute-wise…
This menu item can be used to copy entire data sets of assigned attribute values. The following input window appears (3D model):
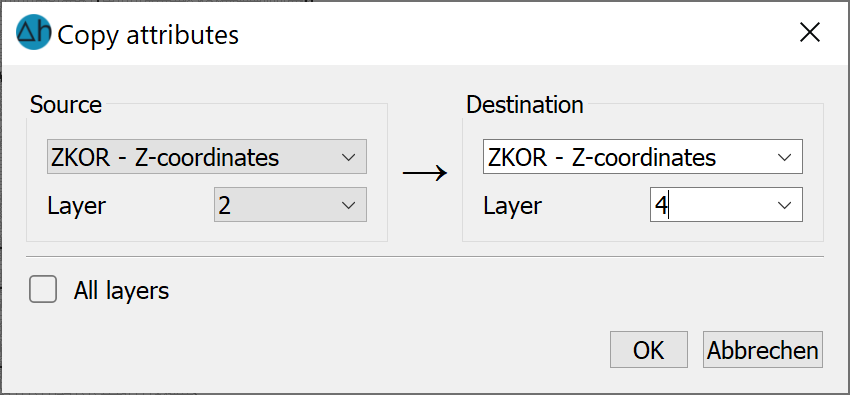
At all nodes or elements where the source data type (source) is present, the node or element receives a further attribute with the identifier of the second data type (target) with the same values and data type.
In a 3D model, it is possible to copy the data layer by layer or for all layers simultaneously.
You can enter any new data identifier (SPRING-compliant designation) as the target data type, but this new data type will have the same properties (e.g. node data, single-occupancy, 2D) as the "source data type".
 Menu item: Stochastical assignment of data
Menu item: Stochastical assignment of data
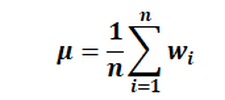
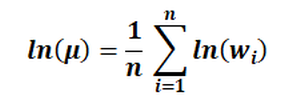
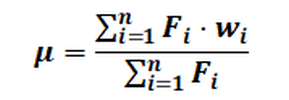 or
or