(Archive fl2.zip)
The second example shows the application of a pit-specific transient boundary condition.
For this purpose, a retention water level elevation (HMAX) and an external water addition quantity (MENG) are defined for each pit. Both parameters can be changed in the transient input file. If water is added from outside to accelerate flooding, the value of the external addition rate must be entered as a positive value. If the value is negative, water is removed from the pit.
The parameters are defined in the dialogue Attributes  Extras
Extras  Flooding parameters...
Flooding parameters...
If a parameter is to be changed during a simulation, it must first be initialised here.
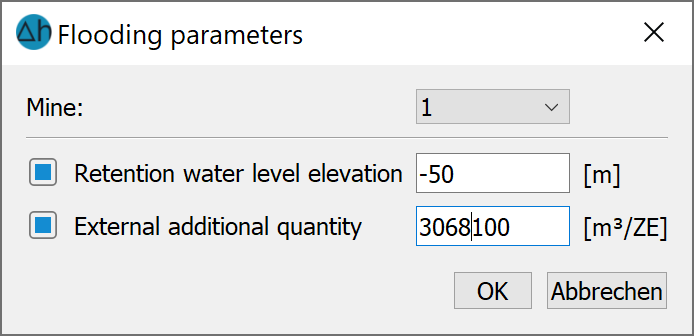
SPRING dialogue for editing the flooding parameters
To show the working of these flooding parameters the following transient boundary conditions were set:
Table 1: Transient boundary conditions (Flooding 2)
|
Date |
Time step |
Boundary condition |
Description |
|
01.01.2012 |
0 |
HMAX = -50 m MENG = 3068100 m³/year |
Start of flooding up to the mine water level at -50 m with a water supply of approx. 8400 m³/day |
|
01.03.2012 |
60 |
MENG = -13149000 m³/year |
Empty pumping of the pit with a pumping capacity of 1500 m³/h = 36000 m³/day) |
|
01.07.2012 |
182 |
HMAX = --46.5 m MENG = 5259600 m³/year |
Further flooding up to the pit water level of -46.5 m with an inflow of approx. 14400 m³/day |
|
01.09.2012 |
244 |
MENG = 0 m³/year |
Flooding without further external addition |
|
31.12.2012 |
365 |
|
End of simulation |
The file with the transient boundary conditions can be found in the archive "fl2.zip" and has the following structure (flooding 2):
# SPRING tutorial
# Flooding
# Simulation 2
ZEITEINHEIT MENG JAHR
BEZUGSDATUM 01.01.2012
DATUM
01.03.2012
MENG #empty mine with pumping rate 1500 m3/hour
1-13149000.
DATUM
01.07.2012
HMAX #restart flooding upto mine water level -46.5m
1 -46.5
MENG #add about 600 m3/hour
1 5259600.
DATUM
01.09.2012
MENG #continue flooding without water supply
1 0.5
The results of this simulation are shown in the following figures. They are based on the files "gruben.csv" and "gruben2.xls" ("fl2.zip").
The boundary condition of the external water supply is represented by the "Potential external water supply" curve (corresponds to the definition of the MENG attribute). The "Actual external water supply" curve represents the volume of water that is pumped in or out depending on the physical conditions of the pit. In particular, the actual and possible external water supply differ between reaching the end of pumping out of the pit and the continuation of flooding.
This is due to the fixed external water supply (MENG = 36000 m³/a), which is no longer available once the pit has been emptied). The current pumping rate after emptying the pit is therefore lower (around 22,000 m³/day.
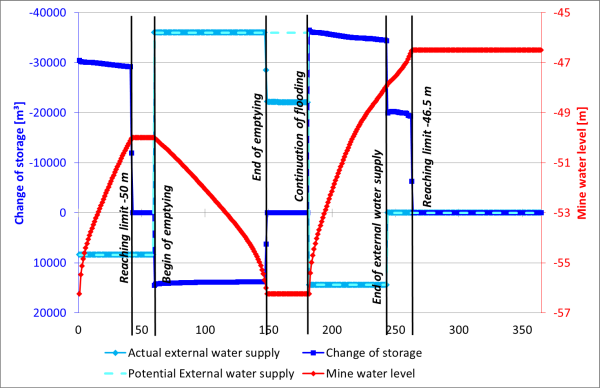
Mine water level, volume change and external water supply (flooding 2)
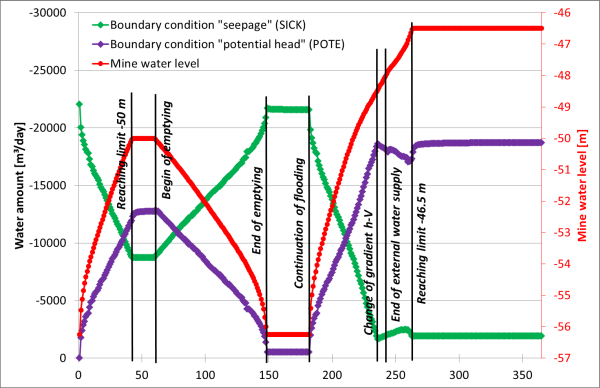
Boundary condition-dependent mass flows (flooding 2)
