If the conservative division is selected, the following input window appears:
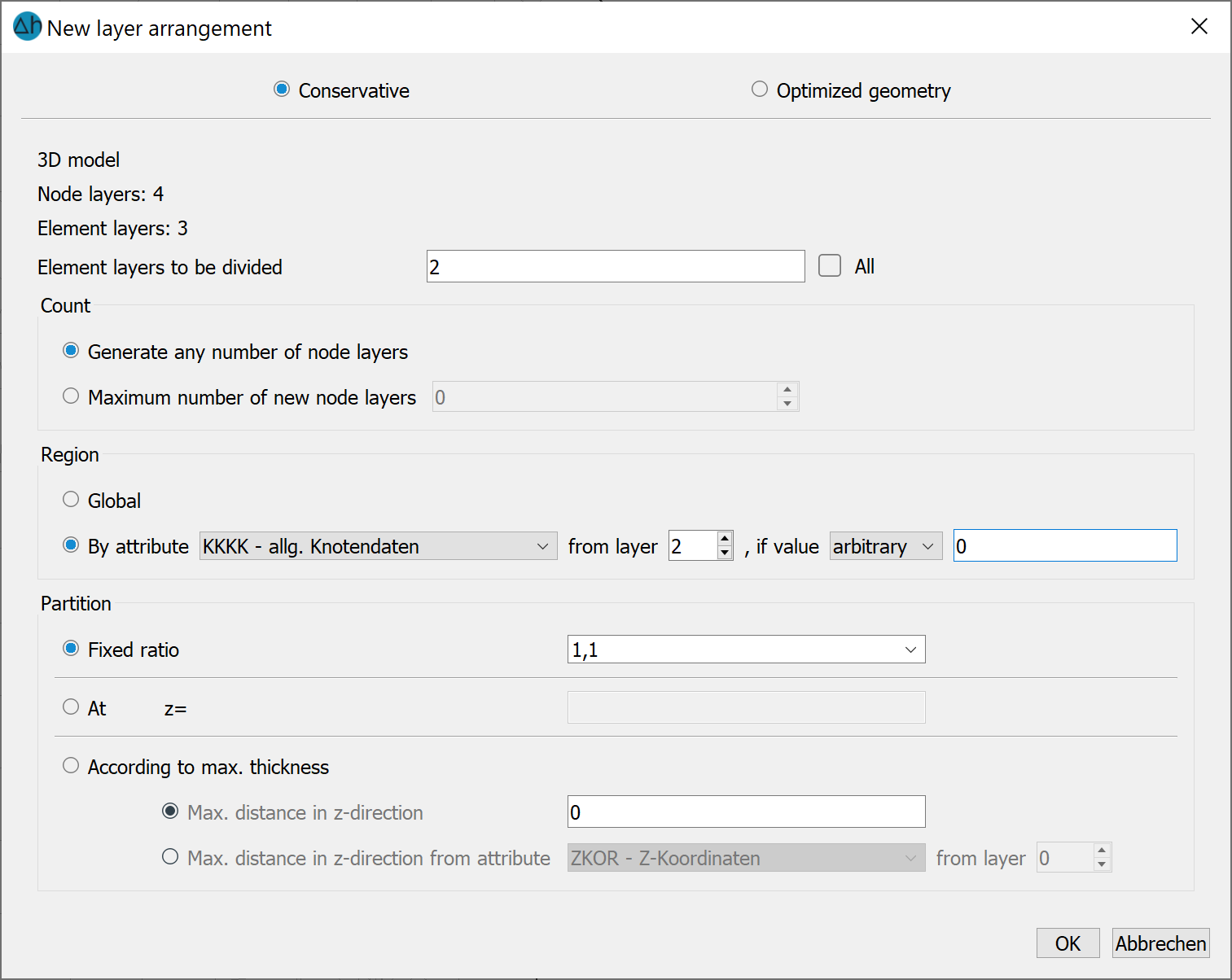
Split layer for local vertical mesh refinement
To illustrate the layer division according to attribute properties by example, the attribute KKKK was assigned to a group of nodes in the second element layer in the 3D model created above.
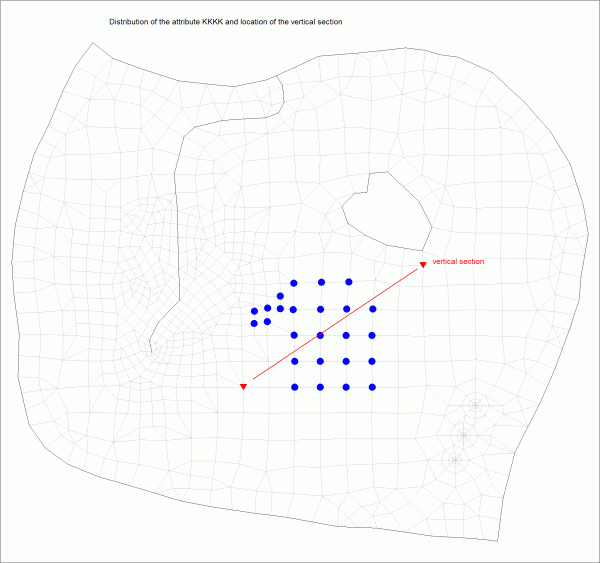
Horizontal view of the nodes with attribute KKKK and position of the vertical section
Firstly, the element layer that will be split must be defined, as it is only ever possible to split a single layer. Layer 2 is selected in this example. By selecting KKKK, the nodes are defined at which a further element layer is now generated. The form in which this is decided by selecting the radio buttons under Partition entitled Fixed ratio, At z = ?, or According to max. thickness.
If the Fixed ratio for division is defined, the number of new layers is identical at all nodes.
When dividing According to maximum thickness, the number of new layers to be inserted is made dependent on the respective layer thickness.
In this example, Fixed ratio was selected with the input "1, 1". This causes an even division of the 2nd element layer into 2 layers with half the thickness of the initial layer.
After saving the project, the new layer division can be displayed with the View  Vertical section menu item. The following image shows the result of the layer division:
Vertical section menu item. The following image shows the result of the layer division:
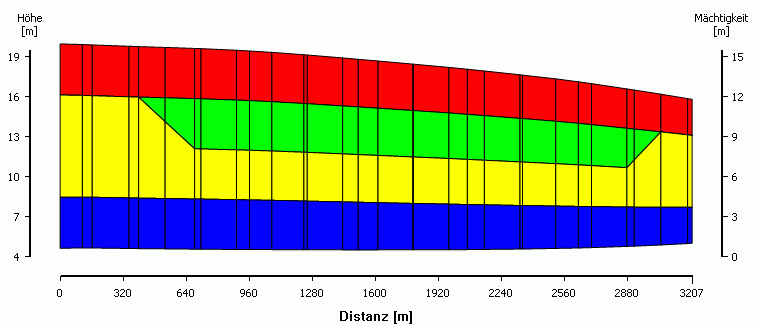
Local vertical mesh refinement of the 2nd element layer where attribute KKKK is present (green area)
If the selected attributes of a node layer only occur sporadically, this results in the following vertical section at the nodes with the corresponding attribute (a ratio of "1, 3" was selected):
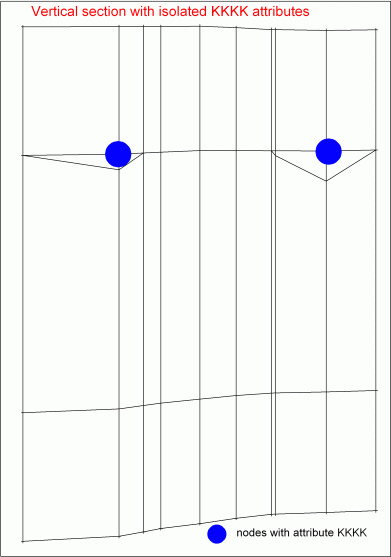
Local vertical mesh refinement of the 2nd element layer if attribute KKKK is only present in isolated cases
The last image shows that the definition via attribute properties is not always useful. If outcropping layers are to be included in a 3D model, manual node or mesh processing based on existing drilling profiles and geological outcrops is usually necessary.
 Optimised geometry layer division
Optimised geometry layer division
