The layer menu is available both in the plot and model mode. It is up to the menu item "New" (plot mode only) identical in both modes. The following menu items are available:
Order
The following submenu appears:
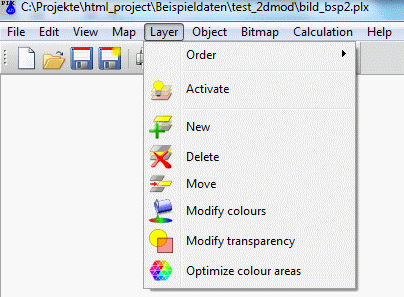
The functions Move forward or rather backward change the position of the layer that it is represented more in the foreground (later) or more in the background (earlier) of the map. The function Move to front puts the layer into the foreground, i.e. it is represented last and covers all other layers in the map. The function Move to back puts the selected layer into the background of the map i. e. it is represented first and is covered by all other layers.
The order of representation for layers can be changed only inside the corresponding map. Therefore, the function Move to front places the layer in the topmost position of the corresponding map and the function Move to back puts the layer in the bottom position of the map. To change the order of two layers belonging to different maps, you must use the corresponding functions for maps. Alternatively, you can merge all loaded maps to one map.
Activate 
This function defines the layer in which the objects created via Object  Edit are inserted or whose properties are to be changed. The layer is identified by choosing an object belonging to it.
Edit are inserted or whose properties are to be changed. The layer is identified by choosing an object belonging to it.
New 
Using this menu item a new, empty layer will be created in a map. On this layer then new objects can be drawn.
Delete 
This function removes the whole layer and every graphic object belonging to it. To identify one of the represented layers, you must capture a graphic object belonging to the layer with the cursor. If there is only one layer, it is automatically removed by activating the function.
Move 
This function provides the possibility to move all objects belonging to one layer at once. The layer is identified with the select cursor and moved by pressing the left mouse button until reaching the new position. For orientation purposes, the bounding box of the layer is shown on the screen.
When multiple cards are opened (plot mode), the layer in the layer list can be moved into another map through the project manager (drag & drop) and the scaling is automatically adjusted to the "goal card" (the layer is overlaid). The map, from which a layer should be moved to a different map, it must contain at least one more layer. If necessary, a new blank layer can be easily created in this map. Subsequently, the layers are shifted.
Modify colours 
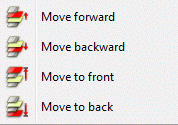
The function Modify colours can re-define single colours. The changes influence only the selected layer. For the case of several layers on the screen, the required layer must be identified using the select cursor. The window where the colour changes are specified appears.
First is to decide whether the choice of colour applies to an object of the layer or the entire layer.
If the existing colour should be changed a colour palette appears by pressing the button according to in which the desired colour can be selected.
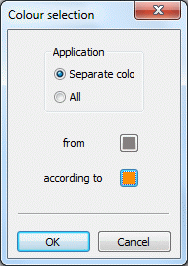
Modify transparency 
The transparency of a layer may be set between "invisible" (= 0, total transparency) and "opaque" (= 255, no transparency) using this input window:
The alternative graphic system, however, must first be enabled in the the menu Edit  Options
Options  In General.
In General.
Optimize colour areas 
In an area plot arise according to the discretization of the elements at first colour-filled polygons. This function provides an algorithm to decrease the number of coloured domains in the current graphic. It optimizes layers with many adjacent polygons of the same colour by merging them into one polygon. The function is typically useful for equal value domains and hatched domains i.e. plots where the attributes for element wise values are represented. The optimization has advantages for data storage as well as for working with data in SPRING. The latter is so because of a much faster graphics-repaint rate. For the case of several layers on the screen, the required layer must be identified using the select cursor. The following window appears:
Before optimizing the layer is divided into n sections in which the areas are first sorted. After that each section is optimized separately, which brings a significant speed advantage. The following applies: The more section areas, the faster the optimization.
