Attribute: MATE [-] (horizontal models only)
As mentioned in the paragraph on zone identification numbers the data type MATE assigns values for permeability and angle to each zone identification number in a horizontal model. The attribute MATE requires necessarily the attribute ZONE (zone numbers).
The unit for the permeability is in this case always m/s.
Example:
ZONE identification number
1 7- 11, 15
10 16- 20
10 1- 6, 12- 14
MATErial data
1 0.005 0.005 0.0
10 0.001 0.0009 30.0
The elements 7-11 and 15 have an equal permeability of 0.005 m/s in both directions without any rotation. The elements 1-6, 12-14 and 16-20 are anisotropic.
The same material all over the model area means one material dataset with any identification number.
An angle different from 0, or different permeabilities for the directions x and y, mean that the corresponding element is not changed during the calibration!
The following figure illustrates the geometric allocation:
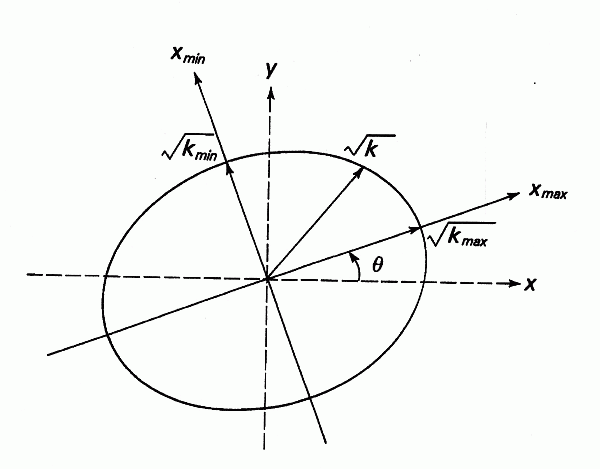
Anisotropy in 2D
The axes Xmax and Xmin denote the axes X and Y which are rotated by the angle Θ. Kmax and Kmin are the maximum and minimum conductivities in the direction of the respective axes. K is the resulting effective conductivity in the direction of flow, which is calculated within the flow calculation.
The anisotropic material values can be entered manually in the *.net file or automatically assigned via the menu item Attributes  Special features
Special features  Anisotropic conductivities....
Anisotropic conductivities....
