The following data must be available for all elements in the model file.
Degree of sealing (attribute VERS, optional): The degree of sealing is specified in the unit [%]. It is required to calculate the sealing-related "rapid" runoff.
Terrain elevation (attribute GELA): The elevation of the elements is automatically calculated from the terrain elevation (previously: attribute NKLH). The elevation is required for the calculation of the grass reference evaporation and refers to the sea level (e.g. m NN, m NHN, mamsl).
Geographical latitude (attribute NKBR): NKBR is required for the calculation of the grass reference evaporation. The unit is [°]. If a coordinate reference system is defined, the geographic latitude is calculated automatically.
Land use (attribute NKFN) [no.]: The land use is specified via the ID assignment in accordance with the definitions in the files for the global location parameters (see below). If no separate definitions are made, the utilisation types correspond to the following table:
|
ID |
Land utilisation |
|
1 |
Grass land |
|
2 |
Farm land |
|
3 |
Garden land |
|
4 |
Tree nursery / orchard |
|
5 |
Running waters |
|
6 |
Standing water |
|
7 |
Housing, industry, commerce, shipping, airport, public facilities, other areas with buildings |
|
8 |
Mixed use (sealed + associated open space, e.g. farm), fallow land |
|
9 |
Stockpile |
|
10 |
Opencast mine, pit, quarry |
|
11 |
Sports, leisure and recreation area, cemetery, playgrounds |
|
12 |
Traffic areas |
|
13 |
Coniferous forest, stand/row of coniferous trees |
|
14 |
Deciduous forest, stand/row of deciduous trees |
|
15 |
Hedges, bushes, orchards |
|
16 |
Mixed forest, tree population/row of deciduous and coniferous trees or without differentiation |
|
17 |
Reeds, reeds |
|
18 |
Unknown utilisation |
|
19 |
Unvegetated area |
|
20 |
Heath |
Soil class (attribute NKBT) [no.]: The soil class is specified via the ID assignment in accordance with the definitions in the files for the global location parameters (see below). If no separate definitions are made, the coding according to BK50 is used with the exception that the attribute NKBT in the model file must NOT = 0. In this case, the user should set NKBT = 1.
Soil type group of the uppermost soil type layer in SPRING based on the definitions of the Geological Service of North Rhine-Westphalia:
0 - Peat, fine humus, artificial material
1 - Loamy-clayey
2 - clayey-loamy
3 - clayey-silty
4 - Sandy-loamy
5 - strongly loamy-sandy
6 - Sandy-silty
7 - Loamy-sandy
8 - Sandy
9 - Low in fine soil
The definition and designation of the soil types according to the Soil Mapping Guide (KA) and the soil type group of the Geological Service of North Rhine-Westphalia is shown in the following table (Source: Geological Service of North Rhine-Westphalia):
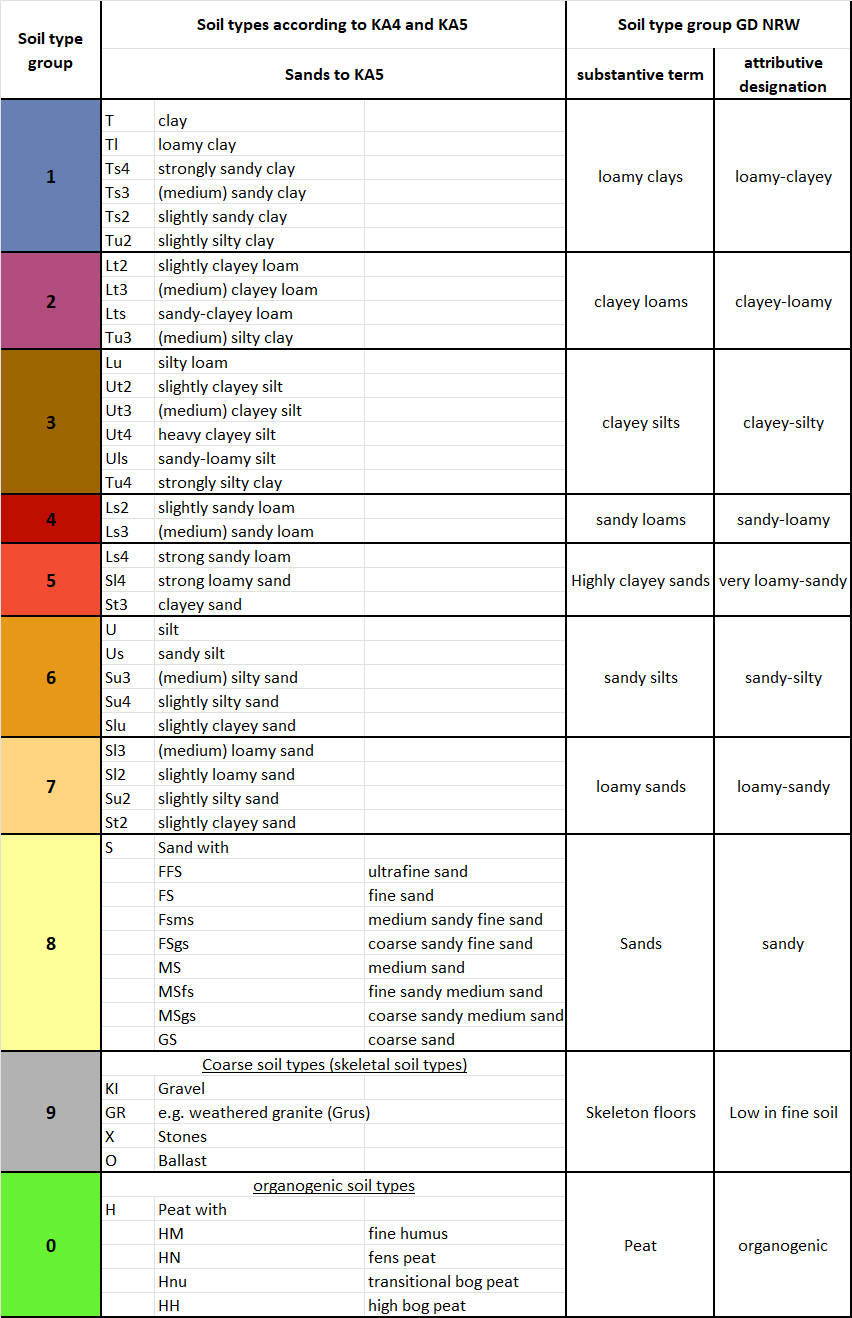
Soil type groups of the Geological Survey of North Rhine-Westphalia
The classification of soil types refers to the upper 40 cm of the upper soil layer.
Climate data ID (attribute NKID) [no.]: A climate data ID must be assigned to the elements for the assignment of the climate data time series. The climate data ID is part of the name of the file that contains the associated climate data for the corresponding element. Example: Climate zone 1008
 NKID = 1008
NKID = 1008  File name = input_id1008.csv. The first column always contains the date, followed by the following options:
File name = input_id1008.csv. The first column always contains the date, followed by the following options:
|
Column name |
Meaning |
Unit |
|
P |
Precipitation |
[mm] |
|
T |
Temperature |
[°C] |
|
S |
Sunshine duration |
[h/d] |
|
Instead of sunshine duration, global radiation is also possible |
||
|
RG |
Global radiation |
[kWh/m²] |
|
ea |
Vapor pressure |
[hPa] |
|
Instead of vapor pressure, relative humidity is also possible |
||
|
RH |
Relative humidity |
[%] |
|
u2 |
Wind speed at 2 m height |
[m/s] |
|
ET0 |
Grass reference evapotranspiration |
[mm/d] |
The column order is arbitrary as long as these labels are followed. When column names differ, compatibility must be maintained, so the order is important in that case.
Date + two columns: P and ET0
Date + five columns: P, T, S or RG, ea or RH, u2
The selection between S or RG or ea or RH is made in the “Advanced Settings” of the respective dialog.
In the RUBINFLUX dialog for the input_ids, the factor for wind speed can be determined by right-clicking.
These time series must be provided by the user. All climate time series must begin with the same start date and be broken down into daily steps. The file directory is queried within the input menu.
Water content at field capacity (attribute NKFK): The water content at field capacity can be determined using the BK50, for example. The unit of the attribute NKFK is [Vol.-%].
Water content at permanent wilting point (attribute NKWP): The water content at permanent wilting point can be determined using the BK50, for example. The unit of the NKWP attribute is [Vol.-%].
Usable field capacity(attribute NNFK): The attribute can be used as an alternative to the two aforementioned attributes, NKFK and NKWP, or in combination. The unit of the attribute NNFK is [Vol.-%].
The following is valid for the calculation:
NKFK and NKWP are defined --> preferred Use
NKFK and NNFK are defined --> Automatic calculation of NKWP = NKFK - NNFK
NNFK and NKWP are defined --> Automatic calculation of NKFK = NNFK + NNWP
only NNFK is defined --> NNFK is used directly
The calculation result is the same for all 4 variants.
For the water content attributes NKWP and NKFK, the following applies contrary to the BK50 classification (e.g. for water surfaces or fillings):
0 < NKWP < NKFK
