The molecular diffusion is a process that occurs independently of the groundwater movement. It is based on the thermal motion of the molecules, the Brownian movement, and leads to a concentration compensation. Only when the concentration of a substance is equal at all points in the groundwater, the diffusion stops.
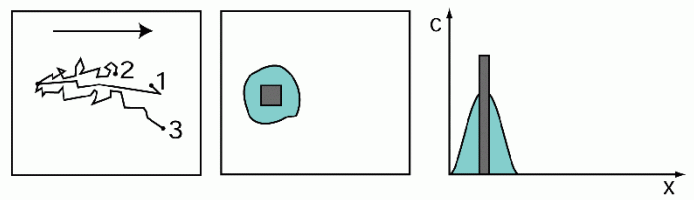
Diffuse mass transport
The mass flux due to molecular diffusion jdiff is described by the 1st Fick's law:
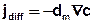
with
dm = molecular diffusion coefficient [m²/s].
Here, the mass flux due to the Brownian movement is proportional to the concentration gradient. Similar to Darcy´s law the negative sign results from the fact that the mass flows from high to low concentrations against the concentration gradient  c.
c.

 Hydromechanical dispersion
Hydromechanical dispersion