This group includes all inflows and outflows, seepage, potential heads, concentrations, well withdrawals, and the like (see figure).
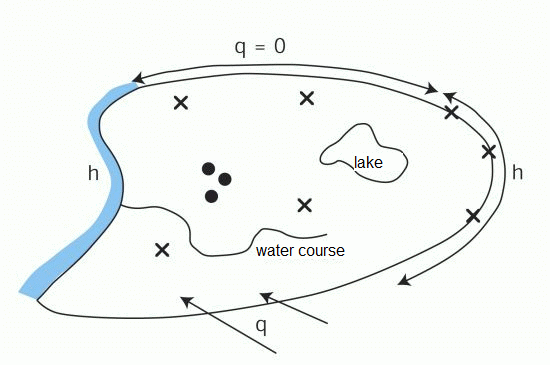
Possible boundary conditions
Minimum required boundary conditions in a flow model:
For at least one node has to be determined either a potential head or a mass flow.
To this node a potential head (attribute POTE) or a lekage boundary (VORF and LERA or LEKN or LEEL in a neighboured element) can be assigned.
For the boundary nodes the following definitions are available:

To a boundary node the attribute POTE (potential) is assigned:
Then the node has a boundary condition of 1st order. (The data types KNOT (sink/sources) or RAND (on-/outflow rates) are not available for this node anymore; inflows FLAE (areal seepage) in horizontal or 3D models in adjacent elements are available.) Inflow or outflow rates across this boundary section are automatically computed from the mass balance.

The attribute POTE is not assigned to a boundary node:
Inflow or outflow rates across the boundary are assigned with the help of KNOT or (boundary condition of 2nd order). In three-dimensional models areal recharge rates (FLAE) are boundary conditions of 2nd order as well. They define an inflow rate across the upper boundary of the model.
No inflow or outflow rates across the boundary are assigned by using KNOT or (or FLAE in an adjacent element for the case of a 3D model). Any inflows and outflows are set to zero (impermeable or no flow boundary).
Regardless whether a potential head POTE was defined for a boundary node or not, the inflow from the top can be defined in a horizontal model with the help of FLAE
The nodes where none of the data types POTE or RAND or KNOT (or FLAE in case of a 3D model) is specified in the input file have a boundary condition of 2nd order i.e. the boundary is set impermeable (e. g. using sheet pile walls or the boundary is perpendicular to the potential lines).
Minimum required boundary conditions in a transport model
For the boundary nodes the following definitions are available:

A fixed concentration 1KON is assigned to the node (boundary condition of 1st order).

At nodes where either an inflow rate from RAND or KNOT or FLAE (in adjacent elements) is defined or a mass flow rate from a fixed potential head is computed or an inflow rate from leakage boundary conditions (LEKN or LERA or LEEL and VORF) exists an inflow concentration KONZ has to be specified. Otherwise it is automatically assumed as zero.

At boundary nodes where an outflow exists, natural boundary conditions are automatically defined, i.e. the dispersive flow across the boundary is set to zero.
