In areas with a groundwater level near the surface this level has to be controlled. Especially in cultivated regions you can do this with drain pipes. The groundwater exfiltrates in these drainages and they drain the water to the next receiving water course.
The following figures show the problem:
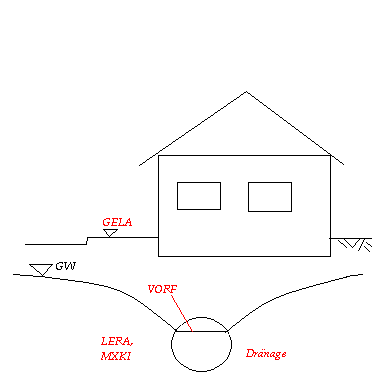
Longitudinal section through a drain pipe in the street
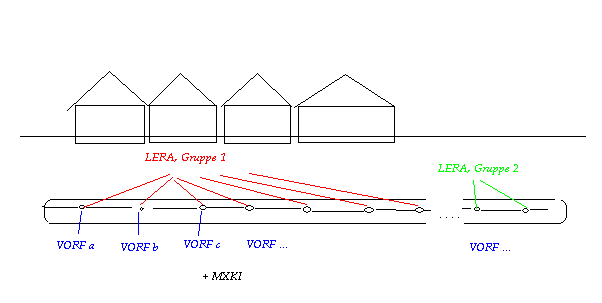
Cross section through a drain pipe in the street
The realization in SPRING looks like this:

VORF
The attribute VORF is assigned to the nodes which represent the drain pipe. The values correspond to the requested level of the groundwater surface (e.g. basement foundations - 0.8 m).

LERA
When modelling a drain pipe the attribute LERA ([m/TU]) has to be assigned to the nodes. It is very important to keep the nodes in order and to separate each drain pipe in different node groups. If discharge rates of the drain pipes exist the leakage coefficient of the drain pipe can be calibrated while comparing the calculated leakage rates with the measured leakage rates. In SPRING you can assign the calculated leakage rates to any attribute (e.g. KKKK) with Attributes  Import result data, selecting the background file "aaa" and selecting "Leakage rate (m³/node/TU)". With Attributes
Import result data, selecting the background file "aaa" and selecting "Leakage rate (m³/node/TU)". With Attributes  Edit nodes
Edit nodes  capture all node attributes are listed, including the leakage rate "KKKK". The summation of the single node rates gets you the total quantity of the calculated runoff of the drain pipe.
capture all node attributes are listed, including the leakage rate "KKKK". The summation of the single node rates gets you the total quantity of the calculated runoff of the drain pipe.

MXKI
If the groundwater level is below the defined value of "VORF", the (empty) drain pipe infiltrates into the groundwater. To prevent that the attribute "MXKI = 0.0" has to be assigned to the nodes of the drain pipe.

MXKE
Sometimes it is necessary to limit the runoff rate to a maximum, e.g. to consider the capacity of the drain pipe. In this case the attribute "MXKE" defines the maximum possible runoff rate. Attention: Taking water out of the model requires a negative value! "MXKE" is defined as m³/TU/m, so a total quantity is given to each drain pipe. The sequence of the nodes must be kept! The maximum value for each node is calculated through the multiplication with the proportionate section between the left and right node.
