In SPRING 7, a newly developed kernel, which works in parallel and is scalable, has been implemented in the software architecture. This leads to the following improvements:
Application with up to 100 million nodes
Fast opening, closing and saving of large models
▪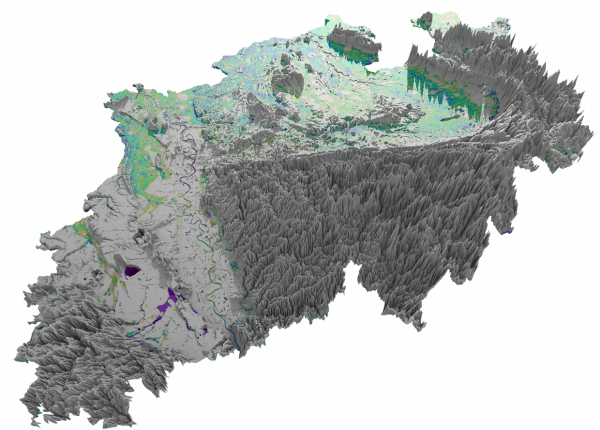
Application with up to 100 million nodes possible
Interpolation algorithms are optimised for scalability with multithreading
New handling of transient data with convenient editing options
Coordinate systems:
Support for coordinate reference systems
Integrated possibilities for coordinate transformation
Connection to map server XYZ&WMS
RUBINFLUX:
Program-assisted generation of Input IDs
Usable field capacity as an alternative to field capacity and permanent wilting point.
Consideration of capillary rise for the coupled calculation of groundwater and RUBINFLUX
Figure "real" soil moisture through coupling (3D: "root zone", multilayer model)
GeoTiff export including clipping of subareas
Saving the transient groundwater recharge (optionally with soil water metrics)
Determination of drought index
Interpolation of climate trend lines
Water systems:
Retention of flood waves using Kalinin-Miljukov
Balancing of runoff components (individual components: base runoff, direct runoff, seepage, external inflow amounts))
Damping of the watercourse flood potentials with Manning-Strickler
Further:
New error estimators
Removable 3D elements within the layering
Energy balance according coupling geothermal utilized boundary conditions
Conditioning for stable solutions of large systems of equations
Optimized matrix structure
Revised measurement point management
Geoprocessing tools
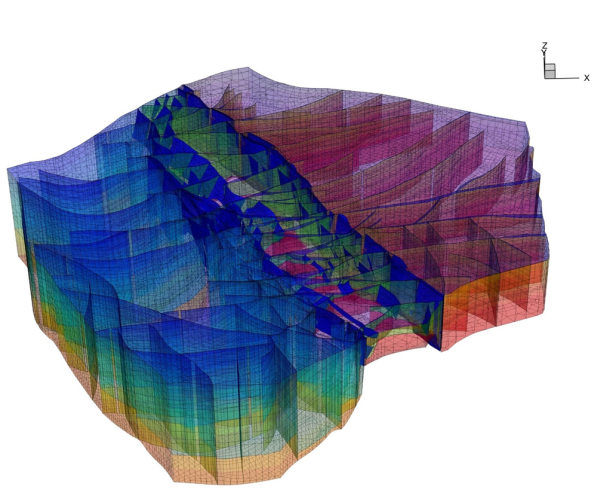
simple transfers of geometries to existing meshes
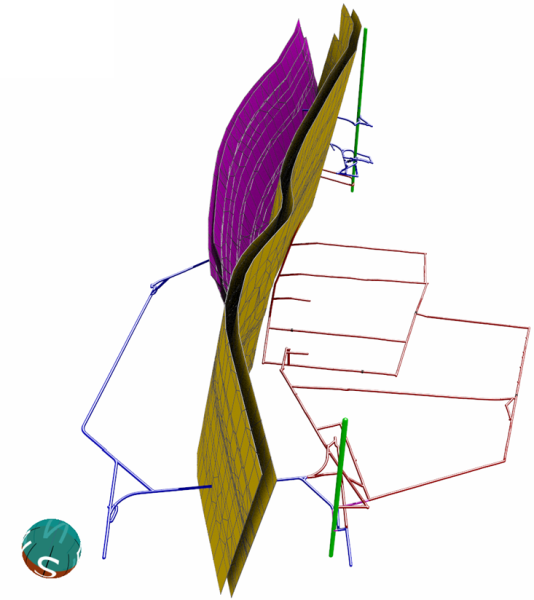
Inclusion of fracture surfaces and advanced geometries in SPRING 7
 SPRING - General Features
SPRING - General Features