The heat flow due to both the thermal conductivity of the fluid jm,w and the matrix jm,s is described by Fourier's law (1822):
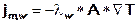 and
and 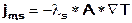
with
jm,w = heat flow in the fluid [W]
jm,s = heat flow in the matrix [W]
λw = thermal conductivity of the fluid [W/(m K)]
λs = thermal conductivity of the matrix [W/(m K)]
A = cross-section of flow [m²]
 T = temperature gradient [K/m]
T = temperature gradient [K/m]
This part of the energy flow is independent of the movement of water. Similar to Darcy`s law, the negative sign results from the fact that the energy flows from high to low temperatures and the temperature gradient is reversed to this.

 Hydromechanic dispersion
Hydromechanic dispersion