In this chapter, a concept for later incorporation of a new structure in an already existing mesh is presented to the user.
Before starting with the edition of the mesh geometry, it is advisable to make copies of the original mesh and structure file. All attribute data affected by deletion of an element area should be saved by clicking on Attributes  Export. A list of all available attribute data is displayed. By selecting the individual attributes, they can be saved as independent "KENN.str" files and then assigned again later on to the modified mesh (interpolated).
Export. A list of all available attribute data is displayed. By selecting the individual attributes, they can be saved as independent "KENN.str" files and then assigned again later on to the modified mesh (interpolated).
Attention! When working with the 3D model, do not forget the data of the 3D file!
After the preliminary work, the stepwise conversion of the model file is started.
Generating the new structure:
Structure  New
New  Lines (at the water course or sheet piling wall)
Lines (at the water course or sheet piling wall)
To visualize a sheet piling wall, it is possible to automatically generate an identical second structure in parallel to the first structure. The distance between the two structures is freely selectable. To do so, select the structure under the menu item Structure  Generate parallel
Generate parallel  Catch/List and determine the side on which the parallel is to be generated with the left mouse button (for area structures, click it on the inside or outside). An input window appears in which the desired distance is entered:
Catch/List and determine the side on which the parallel is to be generated with the left mouse button (for area structures, click it on the inside or outside). An input window appears in which the desired distance is entered:
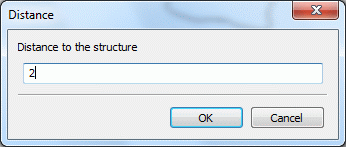
Distance between parallel and structure (m)
After confirmation with right mouse click, the structure appears in the mesh.
The following picture shows a model detail of the new structure along with its parallel (elements and nodes have already been deleted):
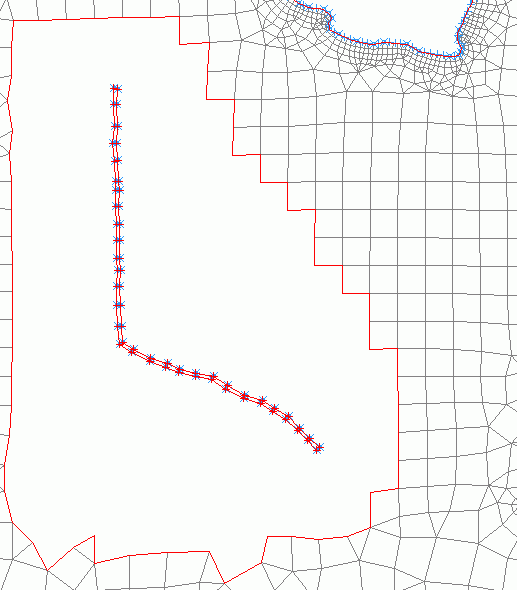
Model with new structure and already assigned contour (blue)
(To make the parallel visible, a distance of 20 m was entered here.)
Deleting elements in the wide-space area of the new structure:
Mesh  Nodes or Elements
Nodes or Elements  Delete
Delete  Area
Area
To apply the new structure as contour:
Contour  New
New  From structure
From structure  Capture
Capture
Generating new mesh nodes:
Mesh  Mesh generation
Mesh generation  Bitmap generation
Bitmap generation Area: Catch mesh nodes: Here it is important to catch the nodes of the existing boundary! The node distance dx should be approximately equal to the existing side length of the elements (in the example, dx = 120.0 m). For neat element grouping, some nodes are inserted manually.
Area: Catch mesh nodes: Here it is important to catch the nodes of the existing boundary! The node distance dx should be approximately equal to the existing side length of the elements (in the example, dx = 120.0 m). For neat element grouping, some nodes are inserted manually.
Note: If a closed contour boundary is present, nodes can only be generated within this contour boundary.
Example: An area in an existing model is deleted, for example, to insert a new building. For this building, a closed contour will be created. Now, it is only possible to generate nodes within this contour. Only if the contour is deleted, nodes can also be generated outside the building.
Generating new elements:
Mesh  Mesh generation
Mesh generation  Element generation
Element generation Triangles and quadrangles from inner edge: The area in which new elements are to be generated can be selected immediately by a single mouse click.
Triangles and quadrangles from inner edge: The area in which new elements are to be generated can be selected immediately by a single mouse click.
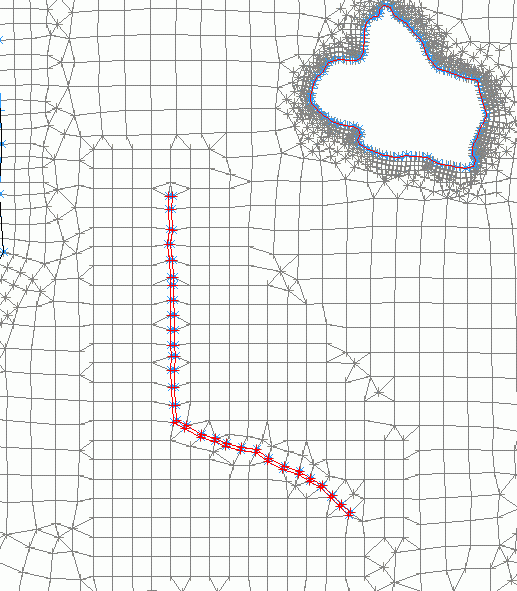
New nodes and elements in the area of the new structure
After completion of the mesh, geometry checks have to be carried out, and the data must be saved!
In the area of the newly generated elements, gaps have been formed in the database.
The missing data must be completed by new assignment of the attributes.
Attributes  Assign
Assign  By interpolation: In the case of large data volumes the saved attribute files must be reduced to the area in question before the new assignment. This is done via Structure
By interpolation: In the case of large data volumes the saved attribute files must be reduced to the area in question before the new assignment. This is done via Structure  Import
Import  *.txt, allocation of the columns and attribute code, and then Structure
*.txt, allocation of the columns and attribute code, and then Structure  Edit
Edit  Delete points: in the area. Pressing the "Invert selection" button in the Catch mode is sufficient for selecting the area to be assigned, while the remainder will be deleted.
Delete points: in the area. Pressing the "Invert selection" button in the Catch mode is sufficient for selecting the area to be assigned, while the remainder will be deleted.
When prompted for the interpolation algorithm, you should select "Gauss", if possible, "Include existing data" and "Filter data with small distance".
Note:
If a local mesh modification has changed the value of only a few nodes, the following procedure is recommended:
If the existing node data of the unmodified nodes are sufficient for interpolation, interpolation without an ASCII file and without additional data from structures is in general only sufficient with "Include existing data". Even when the number of nodes is large, using the Gauss algorithm is suitable for the node data, since prior to interpolation all existing node data that are not in the vicinity of the nodes to be interpolated will be deleted from the interpolation points.
If, due to local mesh modifications, element data (e.g. recharge rates or permeabilities) that are constant within areas must be assigned new values, the following procedure is recommended:
The values can be interpolated without using further ASCII files and without additional data from structures only if the option "Include existing data" is used. By using distance weighting, setting a very large search radius and setting the number of minimum and maximum interpolation points to 1 (exactly one interpolation point), you can ensure that the corresponding elements receive the value of the element assigned with data closest to them.
Step 3: Data assignment  illustrates the different options of data assignment to the finished FE mesh.
illustrates the different options of data assignment to the finished FE mesh.
