1.
Copy the automatically iterated K values to the mesh file
2.
Model checking
3.
Flow calculation
4.
Comparison of the groundwater isolines from the measured data with the calculated groundwater isolines, if available, it will include the display of differences (circle plot) at the measuring points,
5.
Change in the permeabilities by area according to the isoline curves
- if the calculated potentials are too high, then the ground is too impermeable, i.e., it may be necessary to increase the K values
- if the calculated potentials are too low, then the ground does not hold enough water, i.e., it may be necessary to set the K values to less permeability
6.
In addition, there are, of course, other parameters which likewise can be changed by area:
- increasing or reducing the leakage factor of the water courses
- Check inflows from the boundary
- Smoothing of the K values via Attributes  Computation
Computation 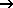 Smooth: Select KWER and set weighting factor, for example, to 0.5. This will balance jumps in adjacent mesh elements.
Smooth: Select KWER and set weighting factor, for example, to 0.5. This will balance jumps in adjacent mesh elements.
 Computation
Computation 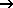 Smooth: Select KWER and set weighting factor, for example, to 0.5. This will balance jumps in adjacent mesh elements.
Smooth: Select KWER and set weighting factor, for example, to 0.5. This will balance jumps in adjacent mesh elements.
After changing the parameters (tip: do not change too many parameters at a time!), the model is inspected, and then a flow calculation is carried out. Then step 4of the schematic procedure is started again. This process is repeated until sufficiently accurate deviations are obtained, and the isoline curves seem plausible.
